FPGA evb – $59 – Cyclone 10 with User Experimental Manual
FII-PRA006/010 User Experimental Manual
Product Only $59
Product URL:
PRA006 – https://fraserinnovations.com/product/altera-fpga-study-board/
PRA010 – https://fraserinnovations.com/product/fpga-study-board-verilog-and-vhdl-for-beginner-cyclone-10-fpga-development-board-with-jtag-embeded-fii-pra010/
Official Shopping Website: https://fpgamarketing.com/FPGA-Study-Board-Verilog-for-beginner-Cyclone-10-FII-PRA006-FII-PRA006.htm
We will send you official newest experimental manuals pdf file, hardware reference guide pdf file, project file zip file, Schematic Diagram pdf file when you order from above links:


The advantage of FPGA evb – Cyclone 10 development board:
- Beginner FPGA study board, cheaper but fully functional. cellphone sized. ( < 100 USD )
- power supply and download at the same time, no extra power supply and no extra data transfer line needed
- Small volume and light and can be put into your pocket. size: 10cm X 7 cm.
- Unique function: can be a study board as well a multifunctional JTAG downloader.
- We use newest version Intel FPGA within two years and you can always keep in the front of FPGA industry.

Altera FPGA Study Board Hardware Resources:
- 6 seven_seg_r
- VGA Video Interface × 1
- 1G Ethernet Interface × 1
- I2C EEPROM × 1
- DIP Switch × 8
- Controllable LED light × 8
- Photoresistance × 1
- Thermistor × 1
- Adjustable Varistor × 1
- Buttons × 4
- GPIO Interface × 2
- Micro usb Interface(Power Supply and downlaod ) × 1
- SPI Communication Interface × 1
- AD/DA Conversion chip × 1
- JTAG Download Interface × 1
- FLASH 32Mbit × 1

Version Control
| Version | Date | Descrption |
| V1.0 | 10/07/2019 | Initial Release |
| V1.1 | 12/07/2019 | Add figures for corresponding experimental phonomena of experiment board |
| V1.2 | 30/08/2019 | Modify part of pin assignments and Ethernet description |
Contents
FII-PRA006/010 User Experimental Manual 0
Project Files Content 5
Part One: Introduction to FII-PRA006/010 1
1、 Design Objective for the System 1
2、 System Resources 1
3、Human-computer Interaction Switch 1
4、Software Development System 1
5、Physical Picture 2
Part Two: FII-PRA006 The Use of Major Hardware Resources and FPGA Development Experiments 4
Experiment 1 LED shifting 5
1.1 Experiment Objective 5
1.2 Experiment Implement 5
1.3 Experiment 5
1.3.1 Introduction to LED 5
1.3.2 Hardware Design 5
1.3.3 Program Design 6
1.4 Experiment Verification 16
1.4.1 Some Preparation Before Verification 16
1.4.2 Method and Steps to Program the Board 19
Experiment 2 SignalTap 21
2.1 Experiment Objective 21
2.2 Experiment Implement 21
2.3 Experiment 21
2.3.1 Introduction to the Switches and SignalTap 21
2.3.2 Hardware Design 21
2.3.3 Program Design 22
2.4 Use and Verification of SignalTap Logic Analyzer 22
Experiment 3 Segment Display 26
3.1 Experiment Objective 26
3.2 Experiment Implement 26
3.3 Experiment 26
3.3.1 Introdyction to the Segment Display 26
3.3.2 Hardware Design 28
3.3.3 Program Design 28
3.4 Application and verification of Flash_memory 32
Experiment 4 Block/SCH Experiment 36
4.1 Experiment Objective 36
4.2 Experiment Implement 36
4.3 Experiment 36
4.4 Experiment Verification 39
Experiment 5 Button Debounce Experiment 40
5.1 Experiment Objective 40
5.2 Experiment Implement 40
5.3 Experiment 40
5.3.1 Introduction to Buttons and Debounce Principle 40
5.3.2 Hardware Design 41
5.3.3 Program Design 42
5.4 Experiment Verification 46
Experiment 6 Use of Multipliers and ModelSim Simulation 48
6.1 Experiment Objective 48
6.2 Experiment Implement 48
6.3 Experiment 48
6.3.1 Introduction of Program 48
6.4 Use of ModelSim and the Experiment Verification 51
Summary and Reflection 59
Experiment 7 Hexadecimal Number to BCD Code Conversion and Application 60
7.1 Experiment Objective 60
7.2 Experiment Implement 60
7.3 Experiment 60
7.2.1 Introduction to the Principle of Converting Hexadecimal Number to BCD Code 60
7.2.2 Introduction of the Program 62
7.4 Application of Hexadecimal Number to BCD Number Conversion 64
7.5 Experiment Verification 65
Experiment Summary and Reflection 67
Experiment 8 Use of ROM 68
8.1 Experiment Objective 68
8.2 Experiment Implement 68
8.3 Experiment 68
8.3.1 Introduction to Program 68
8.4 Experiment Verification 71
Experiment Summary and Reflection 72
Experiment 9 Use Dual_port RAM to Read and Write Frame Data 73
9.1 Experiment Objective 73
9.2 Experiment Implement 73
9.3 Experiment 73
9.3.1 Introduction of the Program 74
9.3 Experiment Verification 82
Experiment Summary and Reflection 83
Experiment 10 Asynchronous Serial Port Design and Experiment 84
10.1 Experiment Objective 84
10.2 Experiment Implement 84
10.3 Experiment 84
10.3.1 Inrtroduction of USB to Serial Conversion Chip (FT2232) 84
10.3.2 Hardware Design 85
10.3.3 Introduction to the Program 85
10.4 Experiment Verification 91
Experiment 11 IIC transmitting Experiment 93
11.1 Experiment Objective 93
11.2 Experiment Implement 93
11.3 Experiment 93
11.3.1 Introduction to EEPROM and IIC Protocol 93
11.3.2 Hardware Introduction 94
11.3.3 Introduction to the Program 94
11.4 Experiment Verification 103
Experiment 12 AD, DA Experiment 106
12.1 Experiment Objective 106
12.2 Experiment Implement 106
12.3 Experiment 106
12.3.1 Introduction to AD Conversion Chip PCF8591 106
12.3.2 Hardware Design 107
12.3.3 Introduction to the Program 108
12.4 Experiment Verification 110
Experiment 13 VGA Experiment 113
13.1 Experiment Objective 113
13.2 Experiment Implement 113
13.2 Experiment 113
13.2.1 VGA Principle 113
13.3.2 Hardware Design 115
13.3.3 Introduction to the Program 115
13.4 Experiment Verification 117
Experiment 14 Ethernet Experiment 119
14.1 Experiment Objective 119
14.2 Experiment Implement 119
14.3 Experiment 119
14.3.1 Experiment Principle 119
14.3.2 Hardware Design 121
14.3.3 Design of the Program 122
14.4 Experiment Verification 140
References 143
Project Files Content
Experiment 1: LED_shifting
Experiment 2: SW_LED
Experiment 3: BCD_counter
Experiment 4: block_counter
Experiment 5: block_debouncing
Experiment 6: mult_sim
Experiment 7: HEX_BCD, HEX_BCD_mult
Experiment 8: memory_rom
Experiment 9: dual_port_ram
Experiment 10: UART_FRAME
Experiment 11: eeprom_test
Experiment 12: adda_test
Experiment 13: vga
Experiment 14: Ethernet
Part One: Introduction to FII-PRA006/010
Design Objective for the System
The main purpose of designing this system is to achieve FPGA learning, development and experiment with Intel Quartus. The main device is Intel Cyclone10 10CL006YE144C8G or 10CL010YE144C8G, and is currently the latest generation of FPGA devices from Intel. The main learning and development projects can be completed as follows:
(1)Basic FPGA design practice
(2)Construction and practice using of SOPC (NIOSII) system.
(3)As a fully functional development board, PRA006/010 can also be used as a downloader to provide download services for Altera, Xillinx, and Risc-V.
System Resources
(1)Serial flash
Spi interface: serial flash (16M bytes)
(2)Serial EEPROM
(3)Gigabit Ethernet: 100/1000 Mbps
(4)USB to serial interface: USB-UART bridge
3、Human-computer Interaction Switch
(1)8 DIP switches
(2)5 buttons
4 buttons are defined as (up, down, left, right), the other one is the reset button
(3)8 LEDs
(4)6 seven-segment display
(5)I2C bus interface
(6)USB to UART interface
(7)JTAG programming interface
(8)2 12-pin GPIO connectors, in line with PMOD interface standards
(9)VGA interface
4、Software Development System
Quartus 18.0 and later versions for FPGA development, Nios-II SOPC
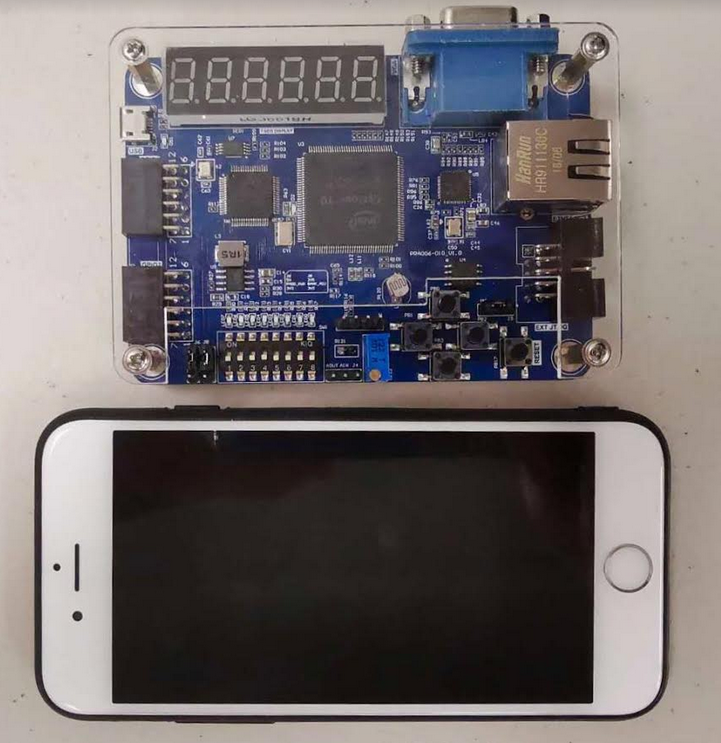
5、Physical Picture
(1)FII-PRA006 system block diagram
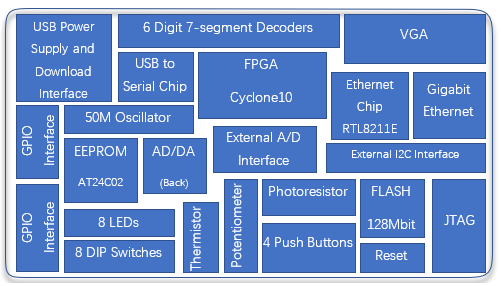
Figure 1 FII-PRA006 system block diagram
(2)FII-PRA006 physical picture
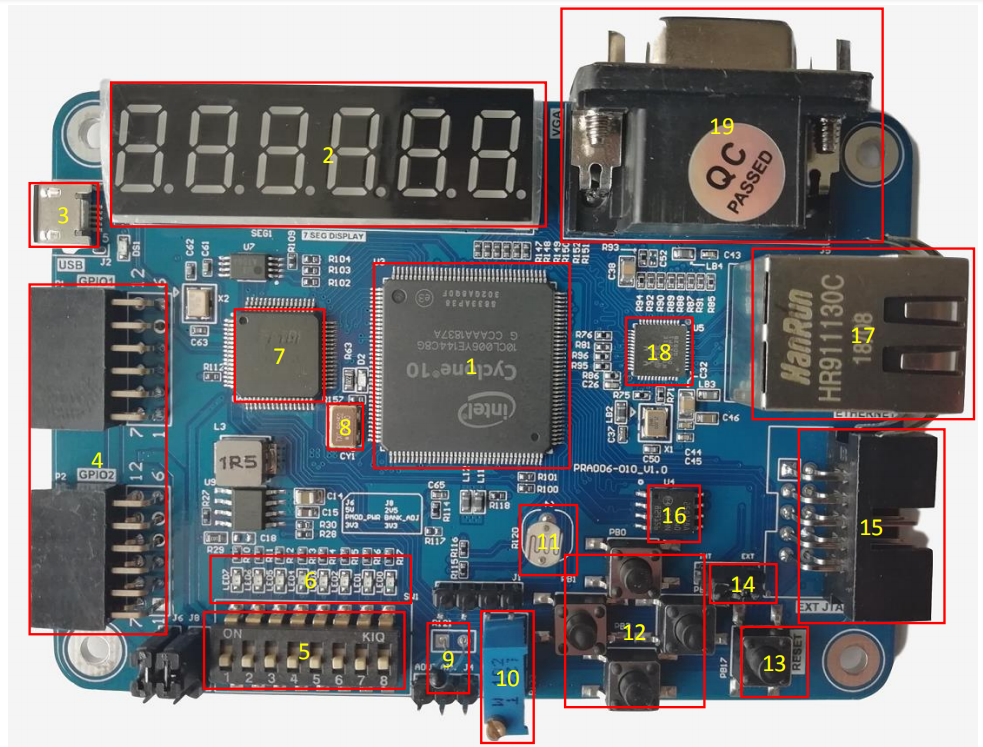
Figure 2 FII-PRA006 physical picture
(3)Corresponding to the physical picture of Figure 2, the main components of the development board are as follows:
1、10CL006YE144C8G or 10CL006YE144C8G
2、6-digit common anode seven-segment display
3、USB power supply and download interface
4、External expansion interface GPIO
5、8 DIP switches
6、8 LEDs
7、USB to serial port chip (FT2232)(Intefrated JTAG download function)
8、50 MHz oscillator
9、Thermistor (NTC-MF52)
10、Potentiometer
11、Photoresistor
12、4 buttons (up, down, right, down)
13、Reset button (Reset)
14、JTAG downloader function conversion interface
15、JTAG download interface (Used only when the board is used as a downloader)
16、Flash (N25Q128A, 128M bit/16M bytes)
17、Ethernet interface
18、Ethernet PHY chip (RTL8211E-VB)
19、VGA interface
20、Back of the board U8: AD/DA conversion chip (PCF8591)
21、Back of the board U13: EEPROM (AT24C02N)
Part Two: FII-PRA006 The Use of Major Hardware Resources and FPGA Development Experiments
This part mainly guides the user to learn the development of the FPGA program and the use of the onboard hardware through the experiment examples of the FPGA. At the same time, the experiment examples are developed from the elementary to the profound to introduction the development system software Quartus II. The experiments covered in this section are as follows.
Experiment 1: LED shifting design experiment
Experiment 2: SignalTap experiment
Experiment 3: Segment display experiment
Experiment 4: Block/SCH experiment
Experiment 5: button debouncing experiment
Experiment 6: use of multiplier and ModelSim simulation
Experiment 7: hex to BCD conversion and application
Experiment 8: usage of ROM
Experiment 9: use dual-ROM to read and write frame data
Experiment 10: asynchrounous serial port design and experiment
Experiment 11: IIC transmission experiment
Experiment 12: AD, DA experiment
Experiment 13: VGA experiment
Experiment 14: Ethernet experiment
Learning exercises in the order of the experimental design, and successfully completing these basic experiments, the level and capabilities of the primary FPGA engineers will be acheived.